Liquid Cooling vs Air Cooling: Which Cooling Method is Better?

Thermal Management Systems: Why Heat Removal Is Essential
In virtually every industrial, scientific, and commercial application where high-performance electronics or sensitive processes are involved, thermal management becomes a mission-critical requirement. Excess heat compromises the reliability, accuracy, and lifespan of devices, especially in high-density configurations or extreme conditions. Whether it's for semiconductor manufacturing, quantum computing, cryogenics, or data centers, advanced cooling for semiconductors and other efficient heat dissipation systems are key to ensuring uninterrupted operation and long-term sustainability.
The primary goal of any cooling system is to extract and relocate heat away from the core components, thereby maintaining a stable, operational temperature. The question frequently asked in this context is: is liquid cooling better than air cooling? The answer depends on various factors, including required temperature ranges, ambient conditions, system configuration, and industry-specific needs.
How Cooling Systems Work
At their core, both air and liquid cooling systems follow a similar thermodynamic principle: transferring heat from a hot surface to a cooler medium (air or liquid), which then dissipates it into the environment. The key difference lies in the method and efficiency of this heat transfer. Mirai Intex leverages air-cycle cooling, also known as the reverse Brayton cycle with recuperator, to deliver efficient and eco-friendly cooling solutions, including MIRAI X Cryo ultra-low-temperature air-cycle systems. You can see the difference on the scheme or air-cycle below.
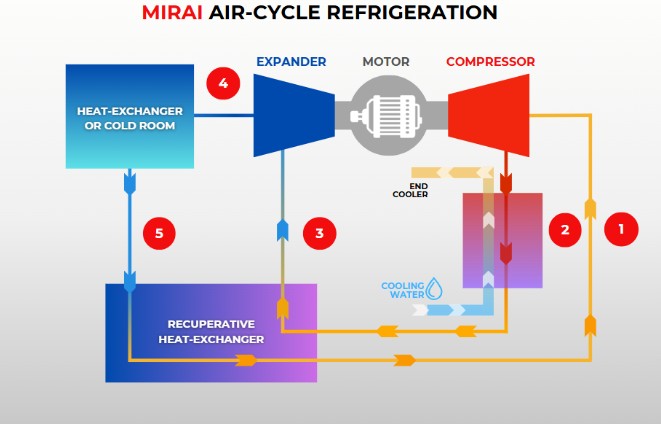
The Process:
- COMPRESSION : Air is compressed, raising its pressure and temperature.
- HEAT EXCHANGE: The compressed air is cooled in a water-cooled heat exchanger.
- RECUPERATION: Air is further cooled in a recuperator by exchanging heat with outgoing air.
- EXPANSION: The cooled air is expanded in a turbo expander, drastically lowering its temperature. This cold air is then used to cool either a chamber (in open-cycle machines) or a heat transfer fluid (in X Cryo and closed-cycle machines).
- RECIRCULATION: The air is reheated in the recuperator and then compressed again, repeating the cycle.
Precision Control:
Synchronous motors with inverter control allow Mirai Intex systems to adjust RPM steplessly, ensuring optimal efficiency and precise part-load operation.
Air Cooling Systems: Simplicity and Accessibility
Air cooling is the most common and historically favored method for thermal management. These systems use fans or blowers to move ambient air over a heat sink attached to a heat-generating component, a principle that also underpins air cooling for cryogenics. The metal fins of the heat sink increase the surface area for better heat exchange.
Advantages:
- Simple setup and lower upfront costs.
- Requires less maintenance.
- Works well for low to moderate thermal loads.
Limitations:
- Typically are less efficient at high thermal loads, but Mirai Intex machines with reverse Bryton cycle demonstrate more efficiency compared to cascade systems.
- While traditional air cooling systems can be noisy and bulky, this is not the case with Mirai Intex machines. Thanks to the innovative design of the turbo-module—where internal parts are magnetically levitated—our systems operate with minimal vibration and exceptionally low noise levels.
In industries where compactness, ultra-low temperature control, and noise reduction are mission-critical, traditional air cooling may fall short. However, Mirai Intex air-based cooling systems break this limitation. Utilizing advanced turbo-module technology and clean air as a refrigerant, our systems deliver exceptional temperature control, energy efficiency, operational reliability, and whisper-quiet performance. This makes them perfectly suited for the most demanding applications—ranging from cryogenics and superconductors to medical and aerospace industries—where precision and environmental responsibility are non-negotiable.
Liquid Cooling Systems: High Efficiency in Demanding Applications
A liquid cooling system uses a coolant—typically water or a specialized fluid—to absorb heat from a heat source. The heated coolant is then pumped through a closed loop to a radiator or heat exchanger, where it releases the absorbed heat. This method is known as a liquid loop system and is a core principle behind closed-cycle refrigeration systems for industrial cooling.
Benefits of Liquid Cooling:
- Superior thermal conductivity of liquid allows faster and more efficient heat transfer.
- Enables precise temperature control.
- Compact design options for space-constrained environments.
- Quieter operation compared to air cooling.
Drawbacks:
- More complex installation.
- Requires pumps and sealing to prevent leaks.
- Higher upfront costs.
It is commonly believed that in the debate of liquid cooling vs air cooling, liquid systems always offer superior efficiency and temperature control—especially in high-performance environments. However, this assumption is increasingly outdated. Modern air-based cooling technologies, such as those developed by Mirai Intex, now rival—and in many cases surpass—liquid systems in terms of precision, reliability, environmental sustainability, and silent operation, even under extreme thermal loads.
Comparative Efficiency: Rethinking Air Cooling Performance
It has long been assumed that liquid cooling systems are inherently more efficient than air-based solutions, largely due to the higher thermal conductivity of liquids like water (approximately 0.6 W/mK compared to air’s 0.025 W/mK). However, this perception no longer holds true in modern industrial practice—especially with the emergence of advanced air cooling technologies, such as those developed by Mirai Intex.
Air, as a refrigerant, offers significant benefits that go beyond thermal conductivity alone. It is clean, dry, non-toxic, non-flammable, and critically, it is not subject to international environmental regulations or phase-outs. This makes it a future-proof and regulatory-compliant option for OEMs and industries worldwide, including applications built around open-cycle systems for industrial process cooling.
Moreover, thanks to the innovative engineering behind Mirai Intex's systems, air cooling can now deliver exceptional temperature stability, high energy efficiency, and near-silent operation, even in applications that traditionally relied on liquid systems. Our turbo-module technology, with magnetically levitating parts, ensures minimal vibration and almost zero maintenance—resulting in low total cost of ownership and operational simplicity.
In short, air is no longer the "basic" option—it is now a high-performance, low-maintenance, and sustainable solution for even the most demanding cooling requirements.
Pros and Cons: Air Cooling vs Liquid Cooling (Revisited)
|
Criteria |
Air Cooling (Advanced, e.g., Mirai Intex) |
Liquid Cooling |
|
Efficiency |
High |
High |
|
Maintenance |
Very Low |
Medium to High |
|
Installation Complexity |
Simple |
Complex |
|
Noise |
Very Low (Mirai) |
Low |
|
Scalability |
High |
High |
|
Precision Temperature Control |
Excellent (Mirai) |
Excellent |
|
Environmental Compliance |
Excellent (no refrigerants) |
Depends on fluid |
|
Cost |
Lower operationally |
Higher (initial and ongoing) |
This updated comparison reflects how far air cooling technology has advanced—particularly when powered by air-cycle refrigeration and innovative design, such as the closed-cycle machines by Mirai Intex.
Applications: Where Each System Excels
Air Cooling (Modern Systems like Mirai Intex):
- Cryogenic freezing and preservation
- Blood plasma freezing & lyophilisation
- Lyophilization
- Semiconductor production and testing with air-cycle cooling for semiconductors
- Biotech and pharmaceutical storage
- Aerospace, laboratory, and medical cooling
- Food and gas liquefaction
Liquid Cooling:
- Immersion-cooled data centers
- Laser cooling in semiconductor manufacturing
- High-density HPC environments
In industries requiring ultra-low temperatures, high precision, minimal noise, and environmental responsibility, air-based solutions from Mirai Intex are not just viable—they’re optimal.
Mirai Intex Solutions:
Mirai Intex specializes in high-efficiency, low-maintenance cooling systems for ultra-low temperature applications. Unlike traditional systems, our units use air as the refrigerant, making them environmentally friendly, regulation-proof, and extremely reliable.
- MIRAI X CRYO series: Offering a wide temperature range cooling systems from +90°C to -160°C, perfect for both heating and ultra-deep freezing applications in research and industry. Heating can help in the defrosting process. Those machines can be used not only for process cooling like lyophilization but also for storage.
- Closed-cycle machines: Cooling systems that are designed for stable operations from -40°C to -160°C, ideal for laboratories and industrial applications requiring consistent negative temp conditions.
- Open-cycle machines: Cooling systems that are designed for stable operations from -40°C to -130°C, ideal for industrial long-term storage solutions requiring consistent negative temp conditions.
All Mirai systems feature oil-free compressors with air-bearings for whisper-quiet, vibration-free operation—making them ideal for sectors where every decibel and degree matters.
Power Consumption and Environmental Impact
As energy prices climb and environmental standards tighten, the choice of a cooling system has long-term consequences. Traditional liquid cooling systems may perform well but often involve fluids with regulatory concerns or higher energy demands in supporting components (pumps, chillers, seals), making sustainable air refrigeration an increasingly attractive alternative.
Mirai Intex’s air-based systems stand out by:
- Using air, a naturally abundant and safe refrigerant, with zero ODP and GWP.
- Eliminating leaks, contamination risks, and costly refrigerant handling.
- Reducing power consumption with oil-free turbo compressors and optimized thermal loops.
- Lowering total environmental footprint through efficient design and minimal servicing.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Cooling Method
So, is liquid cooling better than air cooling? That used to be the case—but not anymore. With the advent of modern air-cycle refrigeration technology, air has become a superior choice for many applications, offering high efficiency, precise control, and unmatched sustainability and future-proof F-gas cooling.
When selecting a cooling setup, OEMs and engineering firms must weigh not only technical performance but also compliance, maintenance, lifecycle costs, and ecological responsibility. With Mirai Intex, you gain access to the most advanced, eco-friendly air cooling solutions on the market, backed by deep engineering expertise and customization capabilities.
For forward-thinking companies, partnering with Mirai Intex means more than just cooling—it means powering innovation with clean, efficient, and future-ready technology.