Air Cycle Technology
MIRAI INTEX leverages advanced air cycle technology, also known as the reverse Brayton cycle with recuperator, to deliver efficient and eco-friendly cooling solutions.
The Process:
1. COMPRESSION : Air is compressed, raising its pressure and temperature.
2. HEAT EXCHANGE: The compressed air is cooled in a water-cooled heat exchanger.
3. RECUPERATION: Air is further cooled in a recuperator by exchanging heat with outgoing air.
4. EXPANSION: The cooled air is expanded in a turbo expander, drastically lowering its temperature. This cold air is then used to cool either a chamber (in open-cycle machines) or a heat transfer fluid (in X Cryo and closed-cycle machines).
5. RECIRCULATION: The air is reheated in the recuperator and then compressed again, repeating the cycle.
Precision Control:
Synchronous motors with inverter control allow MIRAI INTEX systems to adjust RPM steplessly, ensuring optimal efficiency and precise part-load operation.
The Process:
1. COMPRESSION : Air is compressed, raising its pressure and temperature.
2. HEAT EXCHANGE: The compressed air is cooled in a water-cooled heat exchanger.
3. RECUPERATION: Air is further cooled in a recuperator by exchanging heat with outgoing air.
4. EXPANSION: The cooled air is expanded in a turbo expander, drastically lowering its temperature. This cold air is then used to cool either a chamber (in open-cycle machines) or a heat transfer fluid (in X Cryo and closed-cycle machines).
5. RECIRCULATION: The air is reheated in the recuperator and then compressed again, repeating the cycle.
Precision Control:
Synchronous motors with inverter control allow MIRAI INTEX systems to adjust RPM steplessly, ensuring optimal efficiency and precise part-load operation.
Reduced power consumption compared to vapor compression systems by up to
30%
The key feature is the location of turboexpander and compressor are on the same shaft. The energy generated in the expansion process is transferred through the shaft to the compressor, thereby reducing energy consumption by up to 30% compared to vapor compression systems.
Air Bearings
MIRAI INTEX machines don't use traditional friction bearings that require lubrication. Instead, we have developed a new generation of air bearings. These bearings have run for millions of hours, proving their high efficiency and reliability, and ensuring minimal maintenance.
The use of air bearings has allowed us to significantly simplify the compressor design by eliminating oil and does not consume electricity, which increases the efficiency of the compressor and does not expose it to power failures.
The use of air bearings has allowed us to significantly simplify the compressor design by eliminating oil and does not consume electricity, which increases the efficiency of the compressor and does not expose it to power failures.
Snow Catcher
Humidity Extraction Device HED
Machine operates continuously without defrosting procedures that consume operating cooling power and consume additional energy. Humidity Extraction Device traps ice(humid) particles from air in the cold room and extracts it automatically out of the cooling space. Installation of the machine is very simple – only a few holes have to be cut in the cold chamber wall to connect MIRAI Cold and Snow Catcher.
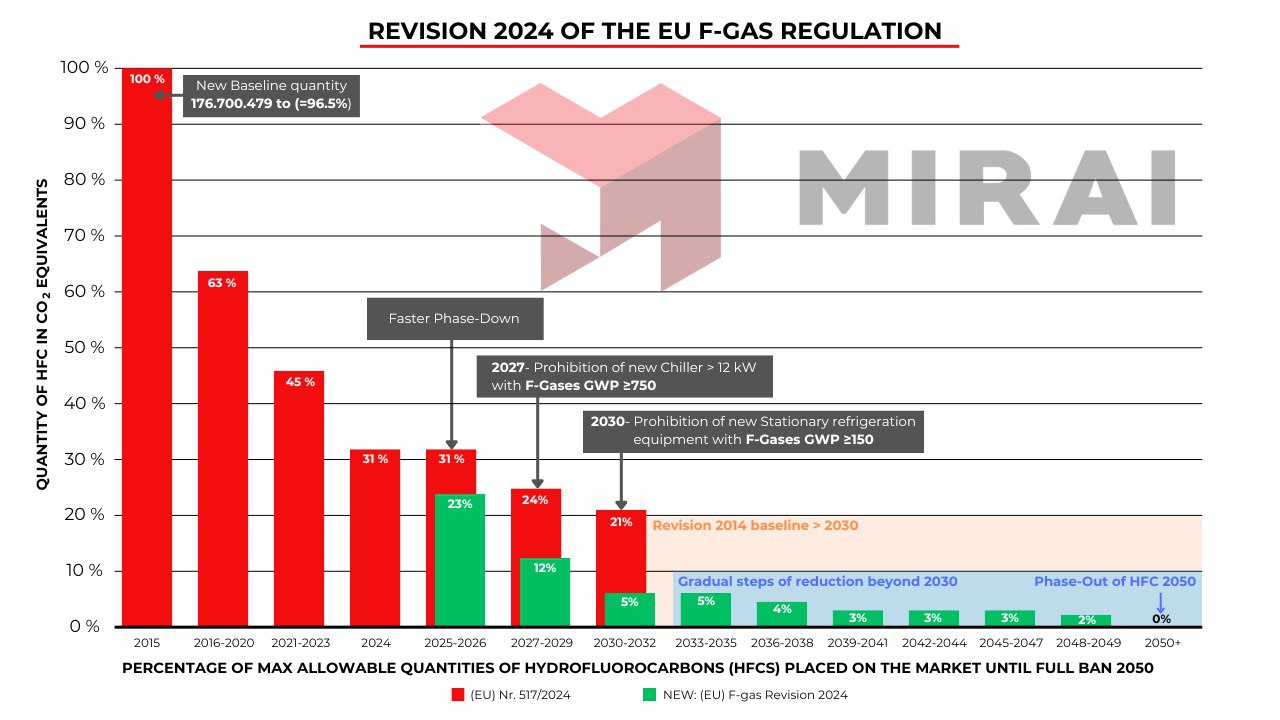
European union F-Gas phase down
The aim of the phased reduction of F-gas emissions is to reduce the usage of HFCs by 95% between 2015 and 2030. We at MIRAI INTEX support our customers with alternative refrigeration solutions, with a GWP ZERO. Air is not a subject of F-gas regulation and is the best substitute to existing refrigerants and offers full refrigeration, capacity and safety.
Eco-Friendly
- Air as refrigerant
- No need to refilling
- Environmentally friendly
Oil free
- No oil in the system due to air bearings
- Reduced costs
Legislative compliance
- Legislative compliance
- Compliance with all international standards / regulations
Operating stability
- Stable loads on power grid and cooling water even in the most demanding conditions
Safe solution
- No chemically active substances
- No risk of fire or explosion
No vibration or noise
- No vibration or noise
- Turbo module design reduces noise and vibrations
Refrigeration Technology
Comparative table
Air Cycle
Vapor Compression
Liquid Nitrogen
Future Proof
Air as refrigerant
Free refrigerant
GWP = 0
Synthetic refrigerants bans
Natural refrigerants restricted by safety regulations
Transport regulations
Storage regulations
Reliability
Air-bearing compressor
No contacting pairs no wear
Compressor wear
Damage by liquid refrigerant
Damage due to insufficient lubrication
No moving parts
High thermal stress
Safety / Machinery room
Low system pressure from 1 to 10 bar
No need for separate machine room
ATEX directive for respective refrigerants
Gas sensors, ventilation
Vibration damping floor
Gas sensors, ventilation
Space for LN2 storage
Maintenance
Only electrical cabinet filter cartridge exchange
Oil and refrigerant management
Safety valves check
Regular leakage check
Trained staff necessary
LN2 refills
Valve function check
Safety valves check
Part load
Frequency inverter included
RPM of compressor controlled automatically
Depending on system design
Usually start / stop or hot gas bypass
Dosage based
Lifecycle Cost
Almost no maintenance required
No refrigerant purchase and refills
Requires many components
Increasing price of refrigerants
Intensive costly maintenance
High long-term running costs
LN2 to be transported and stored on site








