F-gas Regulation update

Introduction to F-Gas Regulation
Fluorinated gases (F-gases) are a family of man-made gases used in a range of industrial and comercial applications due to their valuable properties, including refrigeration, air conditioning, and aerosols. Despite their utility, F-gases have been identified as potent greenhouse gases with a significant impact on global warming. The F-gas Regulation, introduced by the European Union, aims to limit the use of these gases, focusing on containment, use, recovery, and destruction processes to mitigate their environmental impact. This regulation is a critical component of broader efforts to combat climate change, targeting a reduction in the emissions of these high Global Warming Potential (GWP) gases.
The Importance of F-Gas Regulation
F-gases, while constituting a small fraction of total greenhouse gases, have a disproportionately high global warming potential. For example, some F-gases can be thousands of times more potent in trapping heat in the atmosphere than carbon dioxide over a 100-year period. This makes the regulation of F-gases a crucial aspect of global efforts to combat climate change. The F-gas Regulation not only aims to reduce the amount of F-gases released into the atmosphere but also promotes the development and adoption of alternative technologies with lower environmental impacts.
International commitments, such as the Kyoto Protocol and the Paris Agreement, have further underscored the importance of addressing F-gas emissions. By implementing stringent measures and setting ambitious reduction targets, the F-gas Regulation aligns with these global agreements, contributing to the overall goal of limiting global temperature rise. Furthermore, it emphasizes the need for innovation in industries reliant on these gases, pushing for a transition towards more sustainable practices and technologies.
The latest F-gas regulation update
The latest publication of the F-gas emission regulation implies the following:
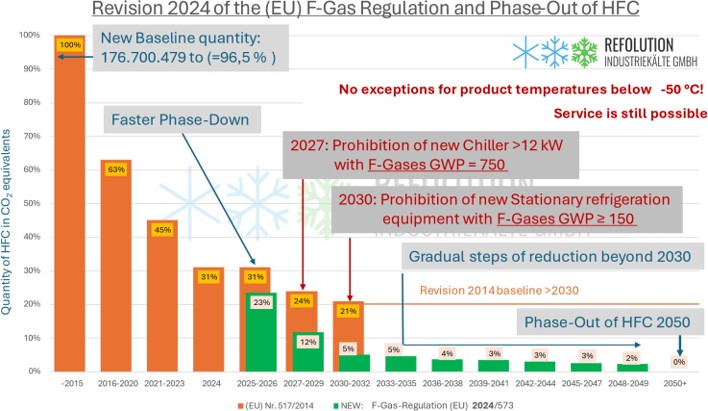
Percentage of maximum allowable quantities of hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs) placed on the market until Full Ban 2050
This chart was created and provided by our partners Refolution
How does this threaten manufacturers who use harmful refrigerants in their production?
Summary of Revision 2024 - EU F-Gas-Regulation
Article 11 - Prohibition of placing products on the market:
(7d) 2027: Chiller with >12 kW with F-Gases GWP = 750! (5c) 2030: Refrigeration equipment with F-Gases GWP ≥150
Exceptions: Chillers or if required to meet safety requirements at the site of operation.
But no Exceptions for product temperatures below -50 °C!
Article 13 - Control of use of F-Gases
2032: Ban of service with virgin refrigerant GWP ≥750
Exceptions: Chillers or for product temperatures below -50 °C, but will be reviewed 2030
The GWP level of some common refrigerants:
- R32 - GWP 675
- R 23 - GWP 14800
- R404A - GWP 3922
- R410A – GWP 2088
- R452A – GWP 2140
Overview of Mirai Intex
Mirai Intex is a company at the forefront of sustainable cooling and refrigeration technology. Specializing in air-based systems, Mirai Intex's mission is to provide environmentally friendly and energy-efficient solutions that comply with and exceed the requirements of the F-gas Regulation. By focusing on innovative air cycle technology, the company offers an alternative to traditional F-gas reliant systems, aligning with global efforts to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and combat climate change.
How Mirai Intex Contributes
Mirai Intex contributes to the objectives of the F-gas Regulation through its development of air cycle technology for cooling and refrigeration. This technology does not rely on F-gases, instead using air as the refrigerant, which has no global warming potential and is completely harmless to the environment. By offering a viable and sustainable alternative to F-gas based machines, Mirai Intex not only aids in reducing the environmental impact of refrigeration and cooling but also promotes a shift in the industry towards greener practices.
The company's products, such as its air cycle refrigeration machines, are designed to be highly efficient, reducing energy consumption and operational costs. This efficiency, combined with the environmental benefits of avoiding F-gases, positions Mirai Intex as a leader in sustainable refrigeration. Additionally, Mirai Intex is involved in research and development activities aimed at further improving the efficiency and applicability of air cycle technology, demonstrating a commitment to innovation and sustainability.
Through partnerships, advocacy, and participation in policy discussions, Mirai Intex also plays a role in shaping the future of environmental regulations and standards. By showcasing the practicality and benefits of air cycle technology, the company encourages the adoption of regulations that favor sustainable alternatives and technologies.
Conclusion
The F-gas Regulation represents a critical effort in the fight against climate change, targeting the reduction of emissions from high global warming potential gases. Mirai Intex stands as a pivotal player in this landscape, offering innovative and sustainable refrigeration and cooling solutions that align with the goals of the F-gas Regulation. Through its focus on air cycle technology, Mirai Intex not only complies with these environmental regulations but also sets a benchmark for the industry's transition towards more sustainable practices. As the world continues to seek solutions to mitigate climate change, the role of companies like Mirai Intex will be increasingly important.
